A flickering LCD monitor is more than just an annoyance. It can cause eye strain, headaches, and a host of other ailments, especially if you spend a great deal of time in front of your computer. Luckily, there are some steps you can take to stop the flickering and avoid these problems. In this article, I’ll show you how to stop your LCD monitor from flickering.
What Causes an LCD Monitor to Flicker
Although your computer monitor may appear to be a still image when no one is using it, it is actually being updated constantly. Much like a film strip is just a bunch of static images displayed quickly, your monitor updates at a fast rate to make it look like things are moving smoothly on the screen. The rate at which your monitor updates is measured in Hertz. One Hertz is equal to one cycle per second. If your monitor is set to update at a rate of 100 Hertz, then it is refreshing 100 times per second. The Hertz used to measure monitor refresh rates is similar to the Gigahertz used to measure the speed of your CPU, except that Gigahertz is a measure expressed in billions of cycles per second.
If the refresh rate on your LCD monitor is set too low, it can appear to be flickering since there aren’t enough updates per second. While some people are comfortable with around 30 Hertz, others can see the flickering and require a higher refresh rate. The most common refresh rate is 60 Hertz. There are other factors that can cause screen flickering and I have mentioned those at the bottom of this post.
Setting the Refresh Rate for an LCD Monitor
The refresh rates that you can set for your LCD monitor are largely determined by the capabilities of your monitor. While some LCD monitors can take advantage of several different refresh rates, others are confined to just one or two. To choose a new refresh rate for your LCD monitor in Windows, begin by clicking on Start > Control Panel > Appearance and Personalization > Display. If you are on Windows 8 or 10, just right-click on the Start button and choose Control Panel. If you’re in icon view, you can click directly on Display.
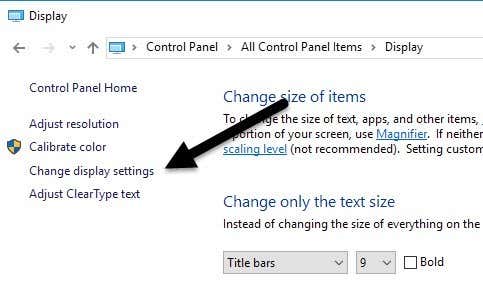
On the left hand side of the window, click on Change Display Settings.
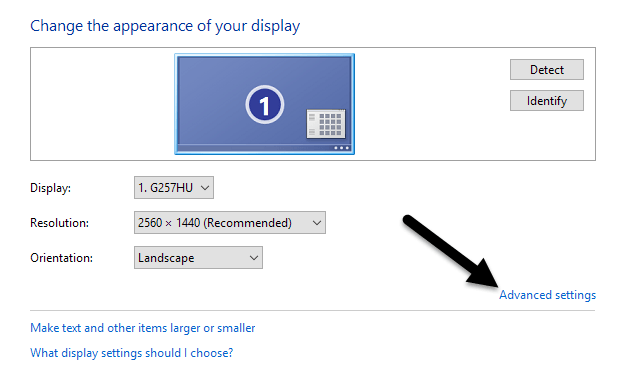
Finally, click on Advanced Settings at the bottom right of the window.
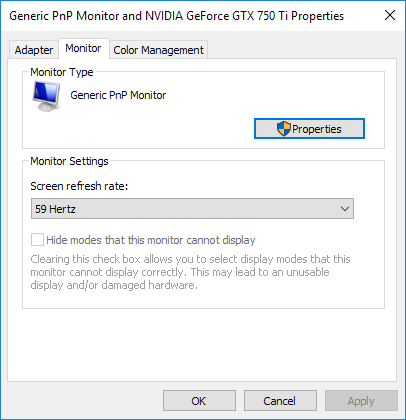
Click on the Monitor tab and you will notice a few things. First, notice the setting labeled Screen Refresh Rate. This is the current refresh rate for your LCD monitor. Click the drop down menu and Windows will display all of the refresh rates possible for your monitor. It is likely that your monitor can only use one or two refresh rates, so this list may not be long. Some manufacturers build monitors that can display anywhere from 30 Hertz to 200 Hertz. Normally, monitors with higher refresh rates will be more expensive. A common refresh rate for gaming monitors is 144 Hertz. If the price of a monitor seems too cheap to you, it’s probably because it has a low refresh rate. For example, some new 4K monitors are cheap, but are only 30 Hertz, which can make everything look choppy on the screen. Also, a lot of monitors will show 59Hz and 60Hz and you can pick between the two. So what’s the difference? It’s basically something to do with rounding and it really doesn’t matter. You can read the exact details on 59Hz vs 60Hz here.
From here, you can try a higher refresh rate and see if the flickering stops. Usually this does the trick. If it doesn’t work or there is only one refresh rate listed, there are two things you can try. First, make sure you are using the latest driver for your LCD monitor. If the driver is outdated or Windows is using a generic driver, the number of refresh rates available may be limited. Visit the manufacturer website and download the latest driver for your version of Windows. If that doesn’t work, you can force Windows to use a refresh rate that is not technically supported by the monitor. Be careful, though, because it is possible to damage your monitor hardware if you do this. On the Monitor tab shown above, there is an option that is checked by default called Hide Modes That This Monitor Cannot Display. By unchecking this option, you can force Windows to use any refresh rate for your monitor that you want. Notice that right underneath this option, Windows warns you about an unusable or damaged display. Uncheck this option and set your monitor to an unsupported refresh rate at your own risk. Depending on your version of Windows, this option may be grayed out, meaning you can only pick from the refresh rates listed in the box. For Mac users running OS X, you can go to System Preferences and click on Display. Here you can change the refresh rate for an external display connected to your Mac.
Other Screen Flickering Causes
If changing the refresh rate doesn’t fix the flicker on the screen, it could be related to other factors. Here is a list of other items you should check: Cable – If you can, change the cable connecting your monitor to your computer. In some cases, a defective cable can cause the signal to break while being transmitted across the wire. Input Port – Another solution is to use a different port on the monitor, if possible. For example, if you are connecting using HDMI, try DVI or DisplayPort or VGA instead and see if that fixes the problem. Surroundings – In addition to hardware issues, electromagnetic fields can also cause screen flickering problems. If you have something else plugged into the same power strip like a heater, fan, etc., try removing it. Video card – If there is an issue with your video card, it will obviously effect the output on the screen. Update the drivers and open your computer to ensure that the video card is properly seated in the slot. Monitor – Lastly, the monitor itself could be damaged or defective. Try connecting the monitor to another computer to see if the problem goes away or remains. Hopefully, this will help you figure out what’s causing the flickering issues with your monitor. If you have any questions, feel free to comment. Enjoy!